Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miyara, Nobukatsu; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-005, 34 Pages, 2017/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is performing the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project, which includes a scientific study of the deep geological environment as a basis of research and development for geological disposal of high level radioactive wastes (HLW), in order to establish comprehensive techniques for the investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment in the sedimentary rock. This report integrates geophysical logging data obtained from the deep borehole investigations (HDB-1  HDB-11) conducted in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project (Phase I).
HDB-11) conducted in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project (Phase I).
Ishikawa, Kiyoshi*; Mezaki, Yoshihiko*; Suzuki, Hideo*; Kai, Masanori*; Watanabe, Hajime*; Fujimori, Seiji*; Ishikawa, Junichi*
JNC TJ7420 99-016, 878 Pages, 1999/06
no abstracts in English
Matsuoka, Kiyoyuki*; Sakurai, Yutaka*
PNC TJ7586 98-002, 63 Pages, 1998/02
None
*; Shingu, Kazuki*; Takahashi, Eiichiro*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*; *; *
PNC TJ7187 97-002, 586 Pages, 1997/11
None
Shingu, Kazuki*; Horinokuchi, Kenji*; Nakajima, Toshihide*
PNC TJ7187 97-001, 170 Pages, 1997/03
no abstracts in English
; ; Sakaki, Toshihiro;
PNC TN7410 94-049, 105 Pages, 1994/09
Excavation of a shaft or a horizontal drift in a rock mass probably affects the rock mass around the openings. It is necessary in the design, construction and safety assessment of underground facilities to consider the properties and extent of the EDZ (Excavation Disturbed Zone; the zone where rock properties and rock conditions have been changed due to excavation). PNC has carried out the in-situ experiments in the Tono mine and has identified the controlling factors in the generation and extent of the EDZ due to blasting. In order to evaluate dependence of the generation and extent of the EDZ on excavation method, Machine Bxcavation Effects Experiment has been started. In FY 1992, a horizontal drift for measurements (measuring drift) was excavated. A horizontal drift parallel to the measuring drift (test drift) is scheduled to be excavated by a machine in FY 1994. The investigations and numerical analysis before excavation of the test drift were carried out in FY 1993. The objectives of the investigations and numerical analysis carried out in FY 1993 are as follows: (1)to measure and evaluate the rock properties and the rock conditions around the test drift before excavation, and (2)to predict by numerical analysis the displacements and stress change during excavation of the test drift. The investigations and numerical analysis in FY 1993 consist of the following items: (1)laboratory tests to measure the compressive strength, deformation modulus, seismic wave velocity, electric resistivity, and so on, (2)in-situ tests to estimate deformability and permeability, (3)borehole wall observation, (4)measurement of the initial stress, (5)seismic tomography and resistivity tomography, and (6)numerical analysis to predict the displacements and stress change by the Finite Blement Method. This report describes the details of these investigations and numerical analysis carried out in FY 1993.
*; Horita, M.*; Ishii, T.*; Yamamoto, Isamu*; Horie, Y.*; Hokari, T.*; *
PNC TJ1060 92-006, 128 Pages, 1992/11
None
Ogata, Nobuhisa*
PNC TN7410 90-005, 35 Pages, 1990/01
In order to establish a hydrogeological model for a rock mass, data is reguired on its hydrogeological properties. A development for geophysical logging technique which is considered to be available for obtaining data on physical properties of rock mass is being carried out aiming at examination of its applicability to a hydrogeological evaluation of the rock mass with a assumption of correspondances between the hydrogeological and the physical properties of the rock mass. In the development of the technique, a borehole was drilled in a granitie rock, followed by measurements of physical parameters by geophysical loggings and laboratory tests on the drill cores and loggings. A consideration is being made on the relationship between the physical properties and the features of fractures and alterations which were obtained by the above methods. The results are as follows : (1)While electric and sonic loggings are found to be available for identification of fracture and alteration zones, micro-resistivity logging is for single fractures. (2)Density-neutron loggings may be useful for detection of fractures with water potentially. (3)The high porosity (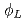 ) zones resulted from density-neutron loggings tend} to correspond to fracture zones with alteration. (4)The high porosity (
) zones resulted from density-neutron loggings tend} to correspond to fracture zones with alteration. (4)The high porosity (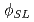 ) zones resulted from sonic logging are likely to correspond to those with high fracture densities regardless of alteration. (5)Division into three rock segments with depth based on the core logging was proved to be compatible with the results of the geophysical logging. Specifically, the features of fracture and alteration correlate with rock classfication and proposity difference (|
) zones resulted from sonic logging are likely to correspond to those with high fracture densities regardless of alteration. (5)Division into three rock segments with depth based on the core logging was proved to be compatible with the results of the geophysical logging. Specifically, the features of fracture and alteration correlate with rock classfication and proposity difference (|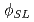 -
- 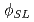 |) in each segment.
|) in each segment.